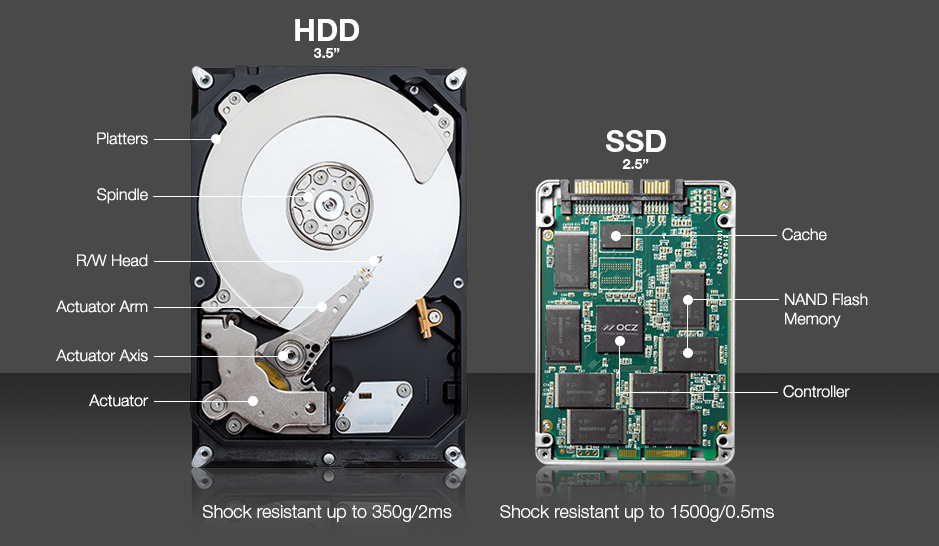
There are two types of drives: HDD (hard disk drive) and SSD (solid-state drive).
HDD and SSD drives
HDD
HDDs are put in in most PCs and laptops. There are many Al plates within the drive. Reading and writing operations are performed due to rotation of the plates and therefore the sensing head placed at some nanometers. The speed of the plates may be as high as 15,000 revolutions per minute which ends within the common noise throughout operation. These drives became common as a result of the supply tons of space (up to 4 TB on a single HDD), high dependableness and stability during reading and writing operations.
Disadvantages of HDDs as compared to SSDs:
. Low speed of reading/writing operations
. High power consumption
. High noise level
HDDs are appropriate for operations that don’t involve frequent reading or writing of knowledge: putting in data storages, backup systems, mail servers, video streams or servers for virtual machines.
SSD
SSDs use memory chips and since they are doing not have any rotating elements, they are utterly silent, consume less power and are smaller than HDDs.
Reading and writing operations are performed faster in SSDs (files are opened, saved and deleted faster).
The relation of the info transfer rate to the size of the transmitted data block is defined by IOPS (Input/output Operations per Second). IOPS shows the amount of blocks which may be read/ written per second. For reference, in hard disk drives this parameter is regarding 80-100 IOPS, whereas in SSDs it’s over 8,000 IOPS.
However, every redaction cycle burns the drive out that shortens its service life.
SSDs are appropriate for high-load comes with various reading and writing operations. SSDs increase the speed of a website developed on any modern CMS.
In order to attach a drive to a server, a drive interface is used.
Interfaces for connecting HDDs
SATA
SATA (Serial Advanced Technology Attachment) may be a serial interface for connecting drives. SATA interface handles giant information volumes at a low speed. This factor, at the side of its low price, is that the reason why it’s currently unremarkably utilized in PCs and server hardware. The speed of SATA interface is up to 600Mb/sec with the turnout of 6 Gb/sec. HDDs with SATA are appropriate for:
Advancement operations, for example, video coding
.Data storage
.Backup system
.Large however not high-load file servers
Drives will be connected via SATA interface on any Intel server (Core i3/i5/i7, Intel Atom, Xeon E3/ Xeon E5, 2 x Xeon E5)
SAS
SAS-(Serial connected SCSI) – may be a serial interface for connecting hard disk drives that relies on SCSI command sets. SAS interface operates at a rate up to 1,200Mb/sec. with the turnout up to 12 Gb/sec. HDDs connected via SAS interface are suitable for prime speed operations with various redaction cycles moreover as:
.Management systems (DMS)
.High loaded web-servers
.Distributed systems
Systems handling numerous queries — terminal servers, 1C-servers.
The disadvantage of SAS is its high price.
SAS interface is available in a pair of x Xeon E5 servers.
Interface for connecting SSDs
SSDs also can be connected via SATA interface. SSDs connected via SATA transmit knowledge at the speed up to 6 Gb/sec.
Some SSDs are connected to the server’s Pie bus directly, thus the name of the interface for SSDs — Pie-SSD. However, such drives are many times a lot of expensive, in order that they aren’t so popular now.
SSDs can also be connected on Intel servers Xeon E3/ Xeon E5, 2 x Xeon E5.
Also read: how Companies Improve their Supply Chains With Artificial intelligence